How to Choose the Right Power Transformer for Your Needs
Table of Contents
Picking the right power transformer is very important for keeping your power system safe, efficient, and working well. This guide explains the basics, different types, important details, and things to think about, helping you choose wisely for what you need.
Understanding Power Transformers: The Basics
What Is a Transformer and What Does It Do?
A transformer is a device used in power systems. Its main job is to change voltage levels – to increase or decrease them – and to separate parts of an electrical circuit. They are essential for moving electrical energy efficiently.
How Does a Transformer Work?
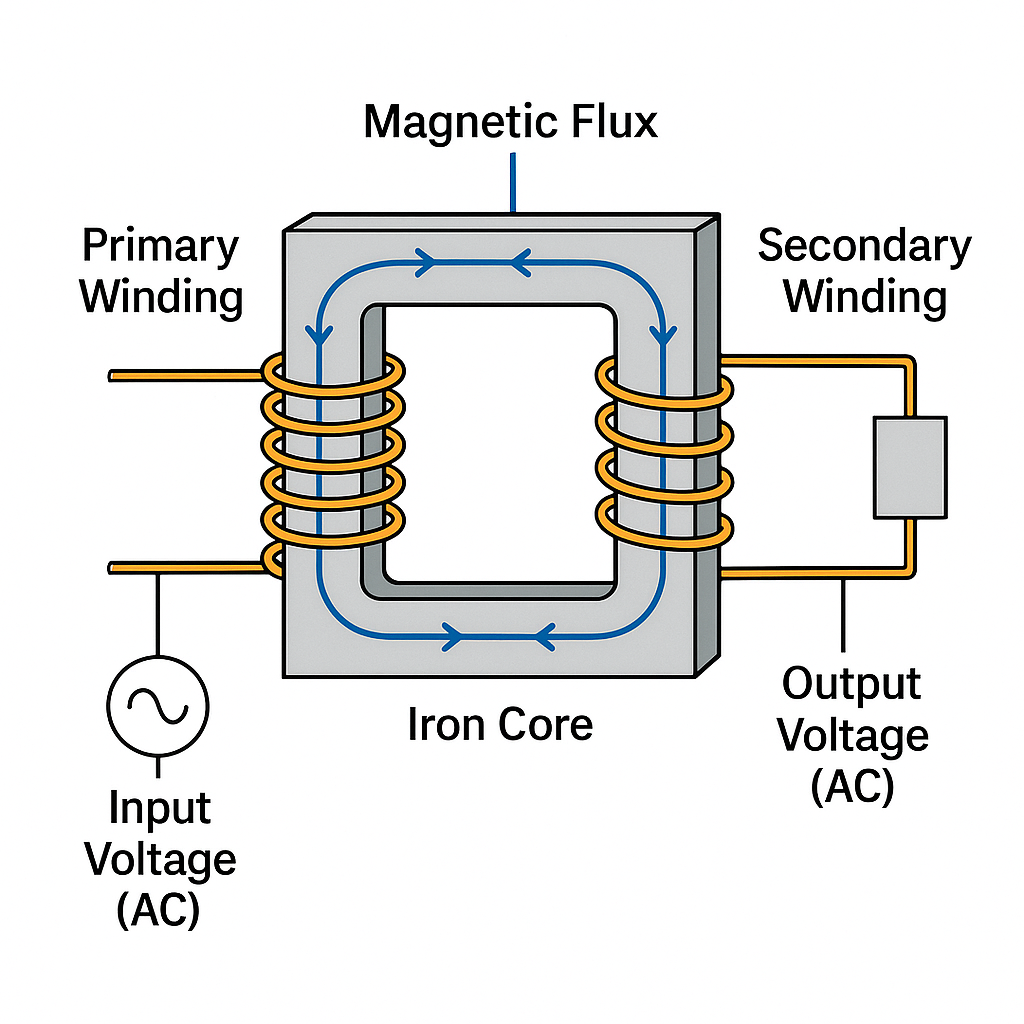
It works using a principle called mutual induction. Electricity flows through primary coils (windings), creating changing magnetic fields in the core. These fields then make electricity flow in the secondary coils (windings) at a different voltage.
Key Parts of a Power Transformer
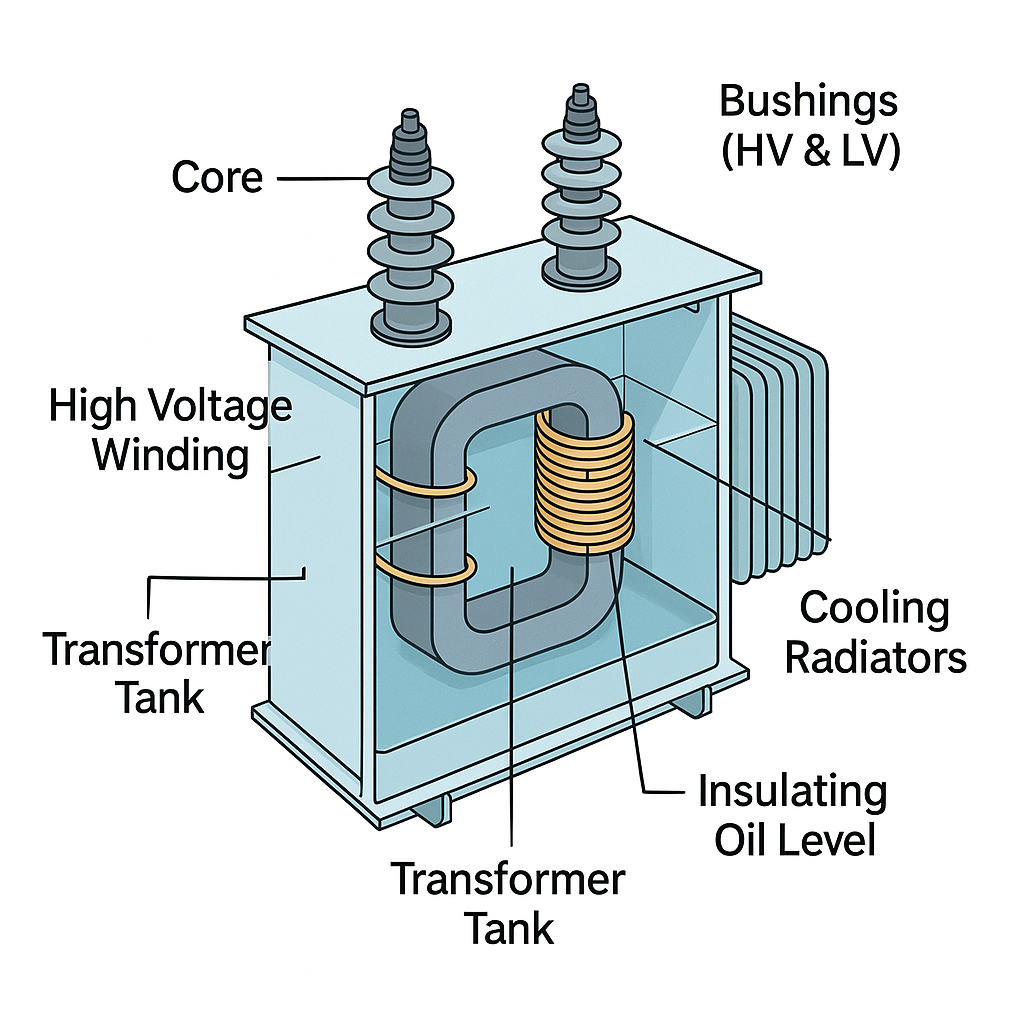
The main parts include the core (usually iron), windings (primary and secondary coils), tank, bushings (where wires connect), cooling system (like radiators or fans), and insulation (like oil or air).
Optional Link: Learn more about transformer core components.
Types of Power Transformers
Types Based on Cooling/Insulation
Oil-Immersed Transformer

- Pros: Excellent cooling, effective insulation.
- Cons: Potential fire hazard, environmental concerns if leaks occur.
- Common Uses: Outdoor installations, substations.
We offer a wide range, including series like SH15, S13, S11, NX2, S NX1, and D.
Link: Explore our range of Oil-Immersed Transformers, including models like the SH15 Three Phase Transformer.
Dry Type Transformers

- Pros: Safer (no oil), less maintenance, better for the environment.
- Cons: Can be bigger, cost more, cooling isn't as strong.
- Common Uses: Indoors or in places needing extra safety.
Cooling might involve natural convection or forced air via fans and potentially an air chute system for directed airflow. We offer series like SCBH15, SCB11, SCB10, SCB NX2, SCB NX1, and DC.
Link: Discover our Dry Type Transformers, such as the SCB10 Three Phase Dry-Type Transformer.
Oil-Immersed vs. Dry-Type: Quick Comparison
| Feature | Oil-Immersed Transformer | Dry Type Transformer |
|---|---|---|
| Cooling/Insulation | Mineral Oil | Air / Cast Resin |
| Efficiency | Generally Higher | Slightly Lower |
| Size/Weight | Often Smaller/Lighter for same rating | Can be Larger/Heavier |
| Location | Typically Outdoors / Substations | Typically Indoors / Sensitive Areas |
| Safety (Fire) | Higher Risk (Flammable Oil) | Lower Risk (Non-flammable) |
| Maintenance | Requires Oil Monitoring/Testing | Lower Maintenance |
| Initial Cost | Generally Lower | Generally Higher |
| Environmental Risk | Potential Oil Leaks | Lower Risk |
For a more detailed analysis, read our full comparison here.
Types Based on Phase
Three Phase Transformer
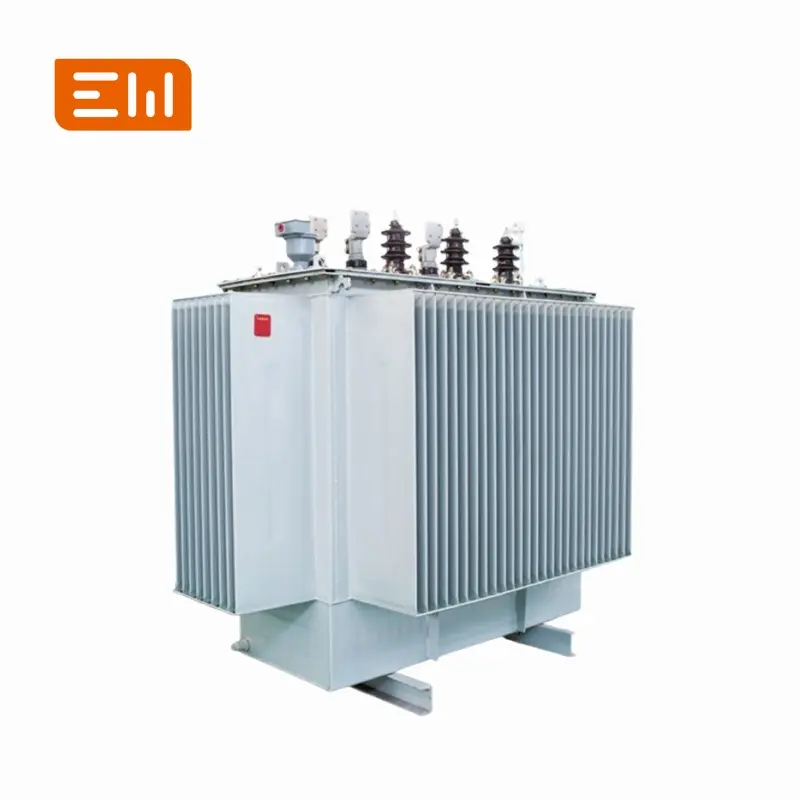
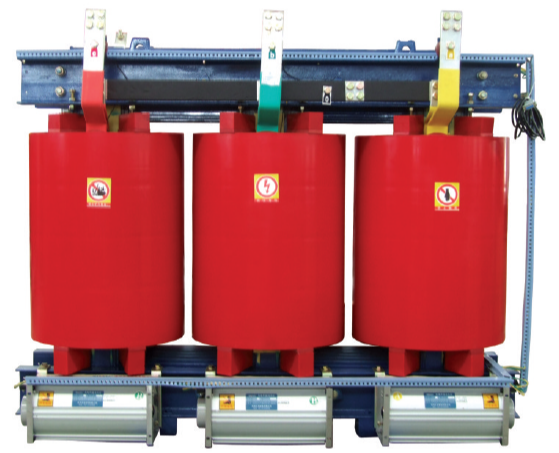


Used commonly for power distribution and in commercial and industrial settings. Most of our products (SH, S, NX, SCBH, SCB series) are this type.
Optional Link: See our three phase oil-immersed and dry-type options.
Single Phase Transformer
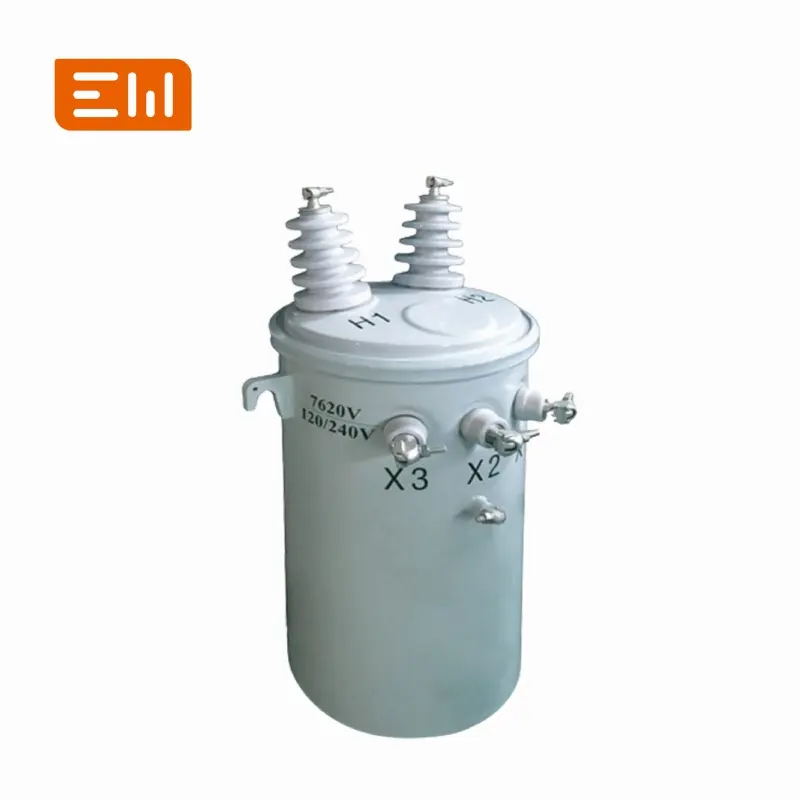
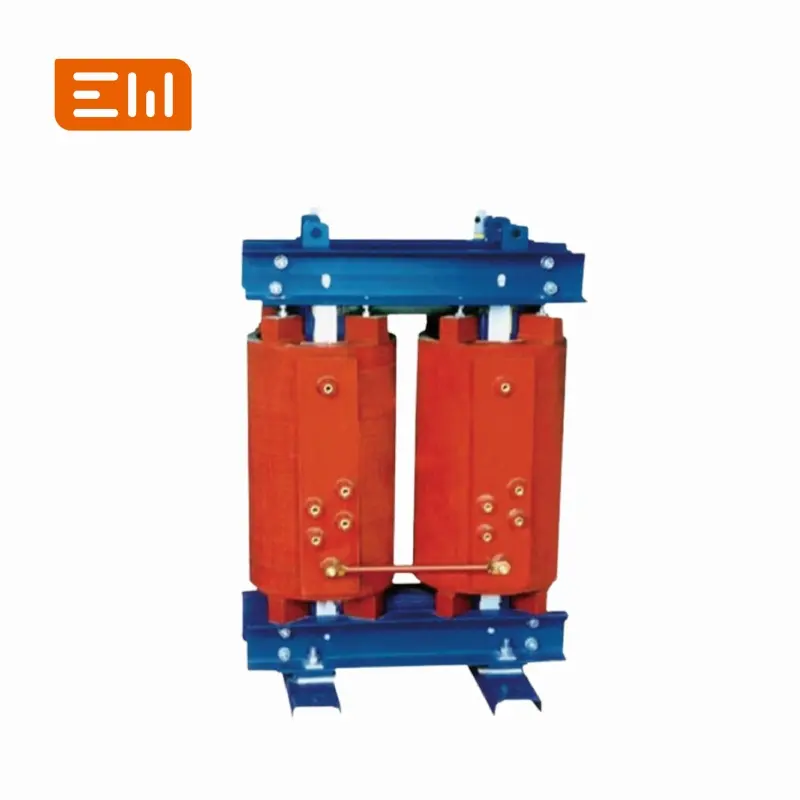


Used for lower voltage needs or specific machines. Our D (Oil-Immersed) and DC (Dry-Type) series are single phase.
Optional Link: Check out our D Single Phase Oil Immersed Transformer and DC Single Phase Dry-Type Transformer.
Types Based on Function (Briefly Mention)
- Step-Up Transformer (Increases voltage)
- Step-Down Transformer (Decreases voltage)
- Distribution Transformer vs. Power Transformer (Explain the difference simply: Power transformers handle very high voltages at power plants, distribution transformers lower voltage for use in homes and businesses)
Understanding Key Transformer Details
- Power Rating (kVA/MVA): Tells you how much power it can handle. This is crucial for matching the transformer to the load it will serve. Our typical range (e.g., 30kVA to 31500kVA) covers a wide range of needs from small commercial to large industrial applications.
- Voltage Ratings (Primary/Secondary, Taps): The input (primary) and output (secondary) voltage levels the transformer is designed for. Taps allow fine-tuning the output voltage to compensate for system variations.
- Phase (Single vs. Three): Matches the electrical system (single-phase for residential/light commercial, three-phase for industrial/heavy commercial).
- Frequency (Hz): Must match the grid frequency (e.g., 50Hz or 60Hz).
- Impedance (%Z): Affects voltage regulation under load and determines the maximum short-circuit current. Important for protection device coordination.
- Cooling Method (e.g., ONAN, ONAF, AN, AF): How heat is dissipated. ONAN (Oil Natural Air Natural), ONAF (Oil Natural Air Forced), AN (Air Natural), AF (Air Forced). Dry types often use AN or AF, sometimes with specialized air chute designs for better airflow.
- Efficiency and Losses: Higher efficiency means less wasted electrical energy (as heat) and lower operating costs. Losses occur in the core (no-load) and windings (load).
- Standards (e.g., IEC, ANSI, GB): Ensures the transformer meets required safety, performance, and dimensional standards for a specific region or application.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Your Transformer
- Matching Electrical Needs: Ensure voltage, kVA/MVA rating, phase, frequency, and impedance align perfectly with your system requirements and load profile.
- Application and Load Type: Consider the environment (commercial and industrial sites, utility grid) and the nature of the load (e.g., constant vs. variable, motor loads, harmonic content).
- Installation Place: Indoor/outdoor, altitude, ambient temperature range, humidity, seismic conditions, and required enclosure protection (IP rating).
- Oil-Immersed vs. Dry-Type Choice: Revisit the pros and cons (safety, maintenance, footprint, cost, environmental impact). Use the detailed comparison to guide your decision.
- Efficiency vs. Cost: Evaluate the total cost of ownership, considering initial purchase price versus long-term energy savings from higher efficiency models.
- Maintenance Needs: Factor in the resources required for upkeep. Oil-filled units typically require more periodic maintenance.
- Supplier Reputation and Support: Choose a reliable manufacturer offering quality products, good warranties, and accessible technical support.
Common Uses for Power Transformers
- Utility Power Grids: Stepping up voltage for transmission and stepping down for distribution.
- Industrial Sites (Factories, Plants): Powering large motors, furnaces, and manufacturing equipment.
- Commercial Buildings (Offices, Malls, Hospitals): Providing appropriate voltage for lighting, HVAC systems, elevators, and office equipment.
- Renewable Energy (Solar Farms, Wind Turbines): Collecting power and stepping up voltage for grid connection.
- Data Centers: Ensuring reliable, conditioned power for servers and cooling systems.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the difference between kVA and kW?
kVA (Kilovolt-Ampere) is apparent power, while kW (Kilowatt) is real power. Transformers are rated in kVA because loads can have different power factors (the ratio of kW to kVA). The kVA rating indicates the total power the transformer can handle, regardless of the load's power factor.
How long does a power transformer typically last?
The lifespan depends on the type, load conditions, maintenance, and environment. Oil-immersed transformers can last 20-40 years or more with proper maintenance. Dry-type transformers often have a similar or slightly shorter lifespan.
Can I use a 60Hz transformer on a 50Hz system?
Generally, no. Operating a transformer at a frequency lower than its design frequency can lead to overheating and core saturation issues. Always use a transformer designed for your system's frequency.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice
Quick Summary
Choosing the right power transformer involves understanding the basics (how they work, key parts), knowing the types (oil-immersed vs. dry-type, single vs. three phase), checking specifications (kVA, voltage, impedance), and considering your specific application and installation environment.
Next Steps
Ready to find the perfect transformer for your needs? Our team is here to help.
Browse Products: Explore our complete range of power transformers.
Get Expert Advice: Contact our transformer specialists today for personalized assistance and a quote.
Table of Contents
- How to Choose the Right Power Transformer for Your Needs
- Table of Contents
- Understanding Power Transformers: The Basics
- Types of Power Transformers
- Understanding Key Transformer Details
- Factors to Consider When Choosing Your Transformer
- Common Uses for Power Transformers
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Conclusion: Making the Right Choice