Comparing Different Types of Transformers: Oil vs Dry Type
In the world of electricity, transformers are super important helpers. Think of them like traffic controllers for electrical power. They help change the power's voltage levels – making it higher or lower – so it can travel long distances or be used safely in homes and buildings with electronic devices. Understanding the different types of transformers is key for anyone working with electricity.
This article will compare two main kinds: the oil type transformer and the dry type transformer. Knowing how they are different helps people choose the right one for the job, making sure things run safely and don't waste energy. We'll look at how they work, where they are used, and what makes each one special.
What Does a Transformer Do?
Imagine electricity flowing like water in pipes. Sometimes you need the pressure (voltage) to be high to push it far, and sometimes you need it lower so it doesn't damage things. That's the main job of power transformers: changing voltage levels. Other types, like voltage transformers, are used for measurement.
They do this using a cool science trick called electromagnetic induction. Inside most transformers, there are special transformer windings – coils of wire wrapped around a core. This core is often made of thin iron plates stacked together, making it one type of iron core transformer. The specific core material affects how well it works. When electricity flows through the first coil (primary winding), it creates an invisible force field called magnetic flux in the core. This changing magnetic flux then causes electricity to flow in the second coil (secondary coil), but at a different voltage! The number of turns in each coil decides if it becomes a step down transformer (lowering voltage) or a step-up transformer (raising voltage). The final voltage you get is the output voltage. While many are three-phase for big power, smaller single phase transformers are common too. Some, like an isolation transformer, are built mainly for safety.
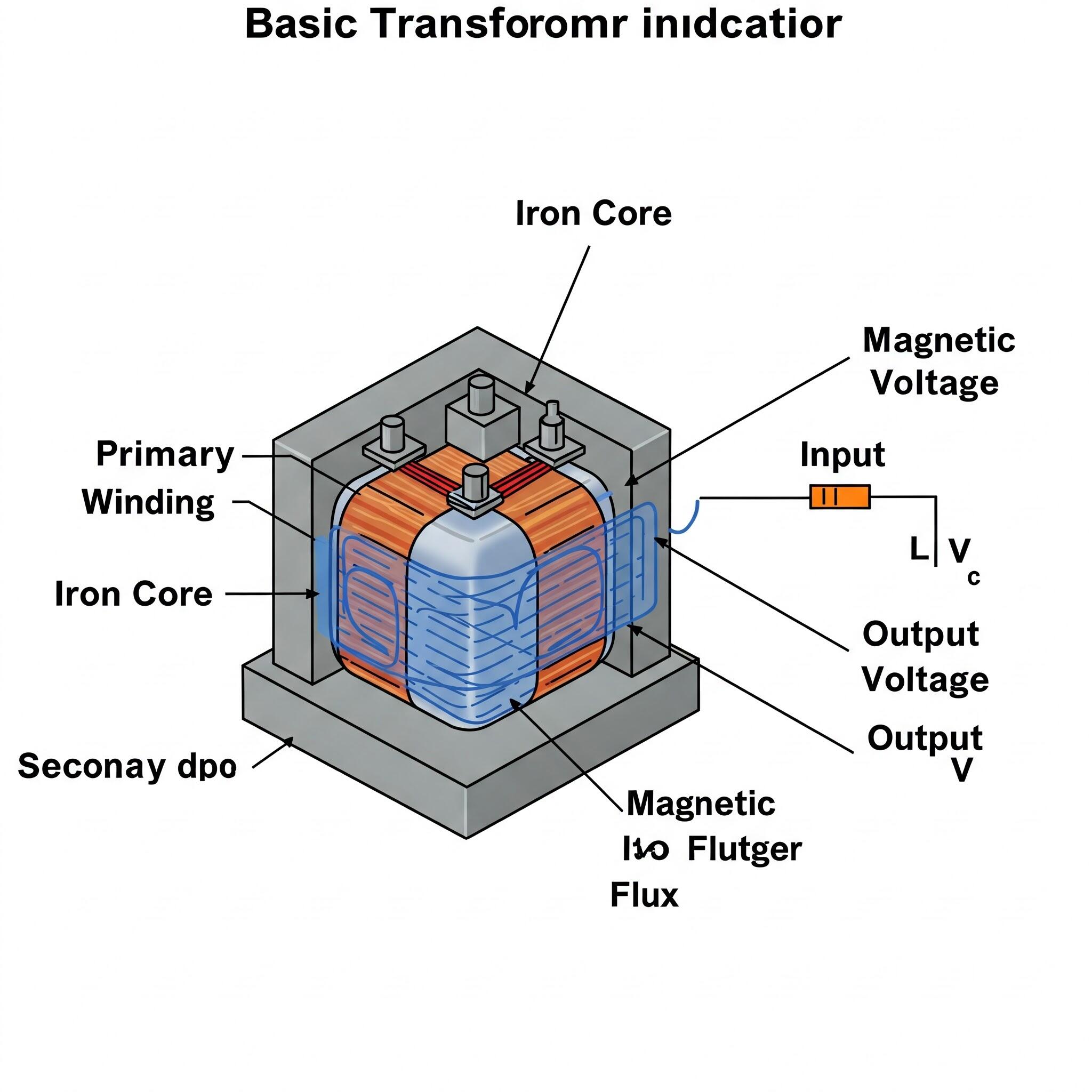
Oil Type Transformers: The Traditional Choice
An oil type transformer uses special oil inside its metal tank. This oil type design has been used for a long time. The oil does two big jobs:
- Cooling: Like coolant in a car, the oil absorbs heat made by the transformer and moves it away, preventing excessive temperature rise and overheating.
- Insulating: The oil stops electricity from jumping between parts where it shouldn't, preventing sparks or damage.
Because the oil works really well for both cooling and insulating, it's a popular choice, especially for large transformers. You can explore our range of Oil-Immersed Transformers to see various models.
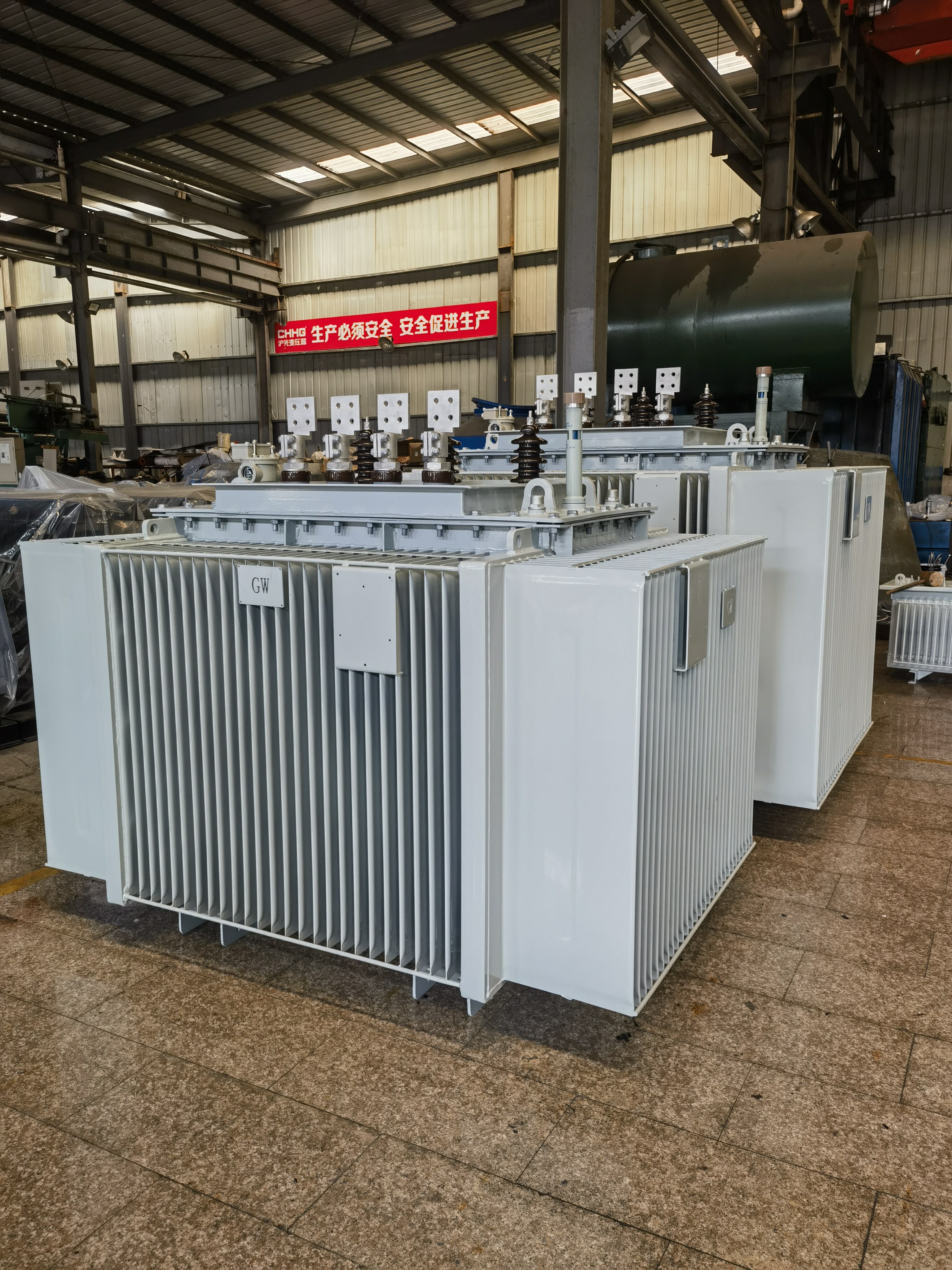

Key Features of Oil Type Transformers
- Effective Cooling: Oil efficiently transfers heat, allowing these transformers to handle high power loads and manage temperature rise effectively.
- Strong Insulation: Provides excellent electrical insulation, suitable for high voltage applications.
- Proven Longevity: With proper oil maintenance, these units can last for decades.
- Cost-Effective (Upfront): Often have a lower initial purchase price compared to dry types, especially for larger kVA ratings.
Where Are Oil Type Transformers Used?
Due to their robust cooling and cost-effectiveness at high power ratings, oil type transformers are commonly found in:
- Utility substations managing power distribution for towns and cities.
- Power generation plants.
- Large industrial facilities (factories, mills) with significant energy demands.
- Outdoor installations where space is less constrained.
They are the workhorses for large-scale power management.
Dry Type Transformers: The Modern & Safer Option
A dry type transformer doesn't use any oil. As the name suggests, it's "dry." It uses air moving around it (natural or forced convection) to cool down and solid insulation materials (like resin or plastic) instead of oil. This dry type design avoids the risks associated with oil. Check out our selection of Dry-Type Transformers, including popular models like the SCB series.
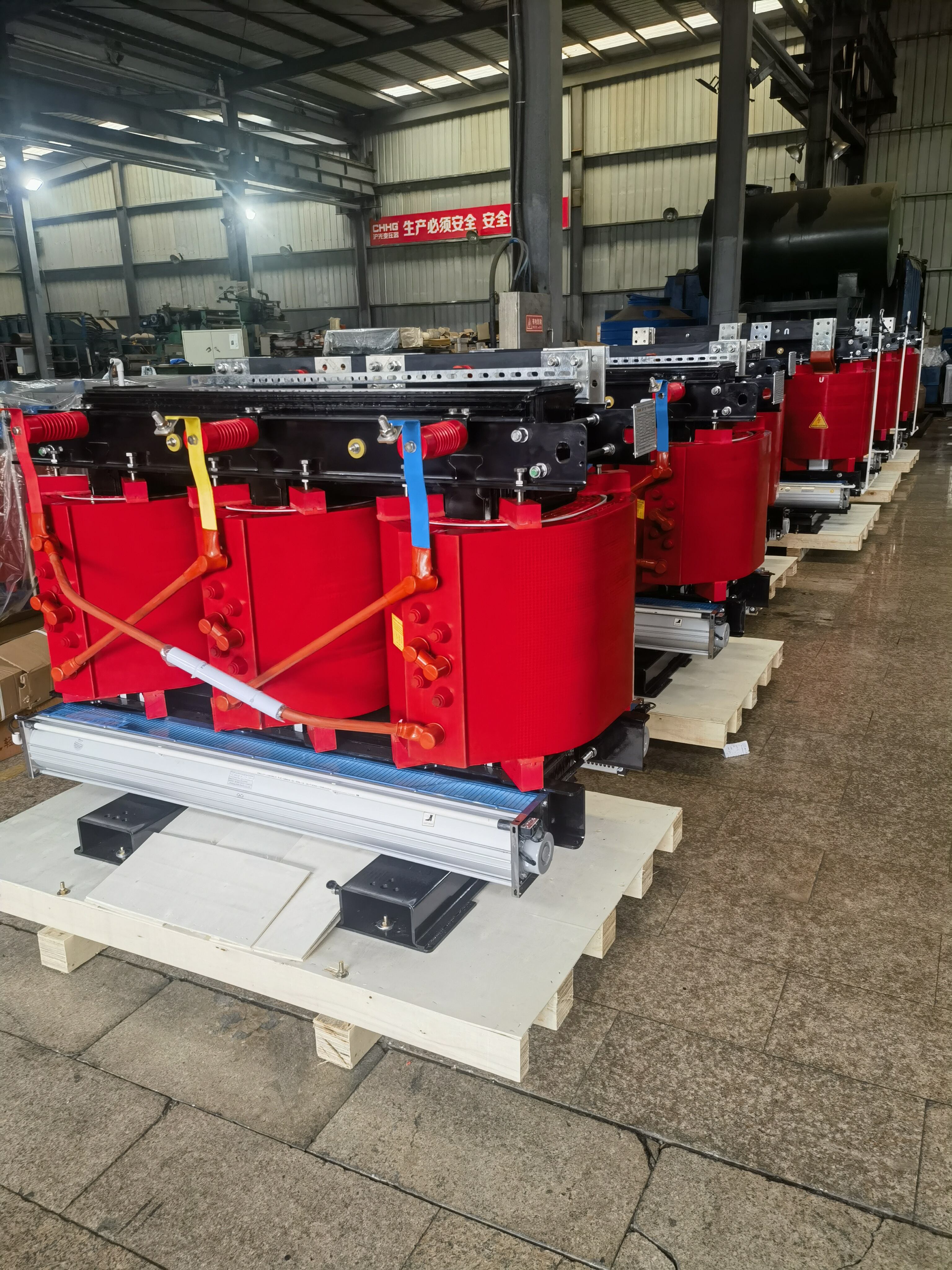

Key Features of Dry Type Transformers
- Environmentally Friendly: No oil means zero risk of leaks or spills harming the environment.
- Enhanced Fire Safety: Eliminates the fire hazard associated with flammable oil, making them ideal for indoor and populated areas.
- Lower Maintenance: No need for oil testing, filtering, or replacement, reducing ongoing upkeep costs.
- Compact Design: Generally smaller and lighter than oil types for the same power rating, saving valuable space.
Where Are Dry Type Transformers Used?
The safety and space-saving features of dry type transformers make them perfect for:
- Indoor installations: Hospitals, schools, offices, shopping malls, data centers.
- Residential buildings and complexes.
- Locations with strict fire codes.
- Environmentally sensitive areas.
- Anywhere space is limited or oil containment is impractical.
Transformers Size Comparison: Does Size Matter?
Yes, size is a critical factor! The transformers size comparison highlights key differences impacting installation.
An oil type transformer is typically larger and heavier due to its oil-filled tank and often external cooling radiators. This requires more installation space, usually outdoors or in dedicated, well-ventilated indoor vaults.
A dry type transformer is generally more compact and lighter. Without the oil and tank, its footprint is smaller, making it easier to install indoors, in smaller electrical rooms, or closer to the load.
Key Size Considerations:
- Location: Indoor vs. outdoor, available floor space, and required clearances for cooling and maintenance.
- Power Rating (kVA): Higher power generally means a larger transformer, but oil types might be slightly smaller for the very highest ratings due to cooling efficiency.
- Weight: Ensure the supporting structure can handle the transformer's weight (oil units are much heavier).
- Regulations: Fire codes often mandate dry type for indoor public spaces, influencing the choice.
Considering the transformers size comparison early helps ensure a smooth installation.
Performance and Efficiency: Which Works Better?
Both different types of transformers effectively change voltage, but have nuances in performance:
- Oil Type Transformers:
- Heat Handling: Superior heat dissipation allows them to handle overloads better and operate reliably near maximum capacity with less risk of excessive temperature rise.
- Efficiency: Can be slightly more efficient at or near full load, especially for very large power transformers.
- Dry Type Transformers:
- Heat Handling: Reliant on air cooling, which is less effective than oil. Good ventilation is crucial, and they may have less overload capacity than oil types.
- Efficiency: Very efficient overall, particularly at partial loads where standby losses can be lower than oil types.
Environmental Impact: Which is Greener?
This is a significant differentiator:
- Oil Type Transformers: The primary concern is potential oil leaks contaminating soil and water. Oil disposal also requires careful environmental management.
- Dry Type Transformers: Much more environmentally friendly. No risk of oil spills. Materials are often easier to recycle.
Cost Considerations: What's the Price Tag?
Evaluate the total cost of ownership: purchase, installation, operation, and maintenance.
- Oil Type Transformers:
- Purchase: Lower upfront cost, especially for high kVA ratings.
- Installation: Can be higher due to size, weight, and potential need for oil containment structures.
- Maintenance: Higher ongoing costs for oil testing, filtering, and potential replacement.
- Operation: Efficient, especially near full load.
- Dry Type Transformers:
- Purchase: Higher upfront cost due to materials and construction.
- Installation: Often lower, particularly indoors, due to smaller size, lighter weight, and no oil containment needs.
- Maintenance: Significantly lower – primarily cleaning and connection checks.
- Operation: Efficient across various loads, potentially lower losses at light loads.
Over the transformer's lifespan, the lower maintenance of a dry type transformer can offset its higher initial price.
Conclusion: Oil Type or Dry Type - Making the Choice
Choosing between an oil type transformer and a dry type transformer depends entirely on your specific needs and installation environment.
- Choose an oil type transformer if:
- Handling very high power is the priority.
- Installation is outdoors or in a suitable industrial setting.
- Upfront cost is the primary driver.
- Regular, specialized maintenance is feasible.
- Choose a dry type transformer if:
- Installation is indoors, especially in public or residential buildings.
- Fire safety is paramount.
- Environmental protection (no oil leaks) is crucial.
- Space is limited (the transformers size comparison favors dry type).
- Lower ongoing maintenance is desired.
Understanding these different types of transformers and weighing factors like safety, cost, location, and maintenance helps you select the best fit, ensuring your power system is safe, reliable, and efficient.
Completing Your Power System: Understanding Transformers
Switchgear plays a vital role in controlling and protecting electrical circuits, but it often works hand-in-hand with transformers to manage voltage levels effectively. Whether you're designing a substation or managing an industrial power setup, understanding how to select the right transformer is just as crucial as choosing the correct switchgear. Our comprehensive guide covers everything you need to know about electric transformers.
Learn More: How to Choose the Right Electric Transformer
Table of Contents
- Comparing Different Types of Transformers: Oil vs Dry Type
- What Does a Transformer Do?
- Oil Type Transformers: The Traditional Choice
- Dry Type Transformers: The Modern & Safer Option
- Transformers Size Comparison: Does Size Matter?
- Performance and Efficiency: Which Works Better?
- Environmental Impact: Which is Greener?
- Cost Considerations: What's the Price Tag?
- Conclusion: Oil Type or Dry Type - Making the Choice
- Completing Your Power System: Understanding Transformers
